!Let Us HELP YOU!
We have a lot of curated content on this blog.
Take this simple 20 second Quiz to Help You
Find The Exact Content You Are Looking For!
Do you want to learn How To Make Beats in Ableton? If yes, this is the right destination for you! This informative material will highlight the touchstone characteristics and methods of Ableton 12 that can help your musical thoughts materialize. Be you a total newcomer or someone perfecting your ability, the manual offers you the fullest spectrum of materials.I curated this article with the help of this amazing video The NEW Ableton 12 Beginner Guide (in 22 Minutes) from Ethan Davis's YouTube Channel which speicalizes in making beats in Ableton.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Ableton
Ableton Live is a digital audio workstation (DAW) that is so powerful it has almost changed the way we create music. It is more than a piece of software; it is a tool for creative expression and helps you compose, mix, and perform music with ease. Ableton is an excellent choice for both pro music producers and their peers who are just starting out which is because it has a simple user interface combined with complex cutting-edge features that meet the demands of all knowledge and experience levels.
Its incomparable Session and Arrangement Views make it easy for the user to instantly turn from live performance to traditional studio recording. The result is that electronic music producers and DJs consider it the primary choice. Making beats in Ableton and learning its essential features are the first steps to success.
Setting Up Your First Project
It is easy to get started with Ableton. By launching the software, you will find that it often opens with a demo song. This is a great way to explore its features. You would, however, need to start your project by opening File > New Live Set first. This action will give you an empty canvas to create your art on.
Right before you plunge into making music, the very first thing is to set up your choices in the right manner. Just hit Command + , or you can go to Live > Preferences. In this section, make sure that the audio input and output devices are set correctly, and also adjust your sample rate. In the case of most projects, a sample rate of 44.1 kHz is accurate, yet you have the option to select 48 kHz if you would like.
Adjusting Preferences for Optimal Performance
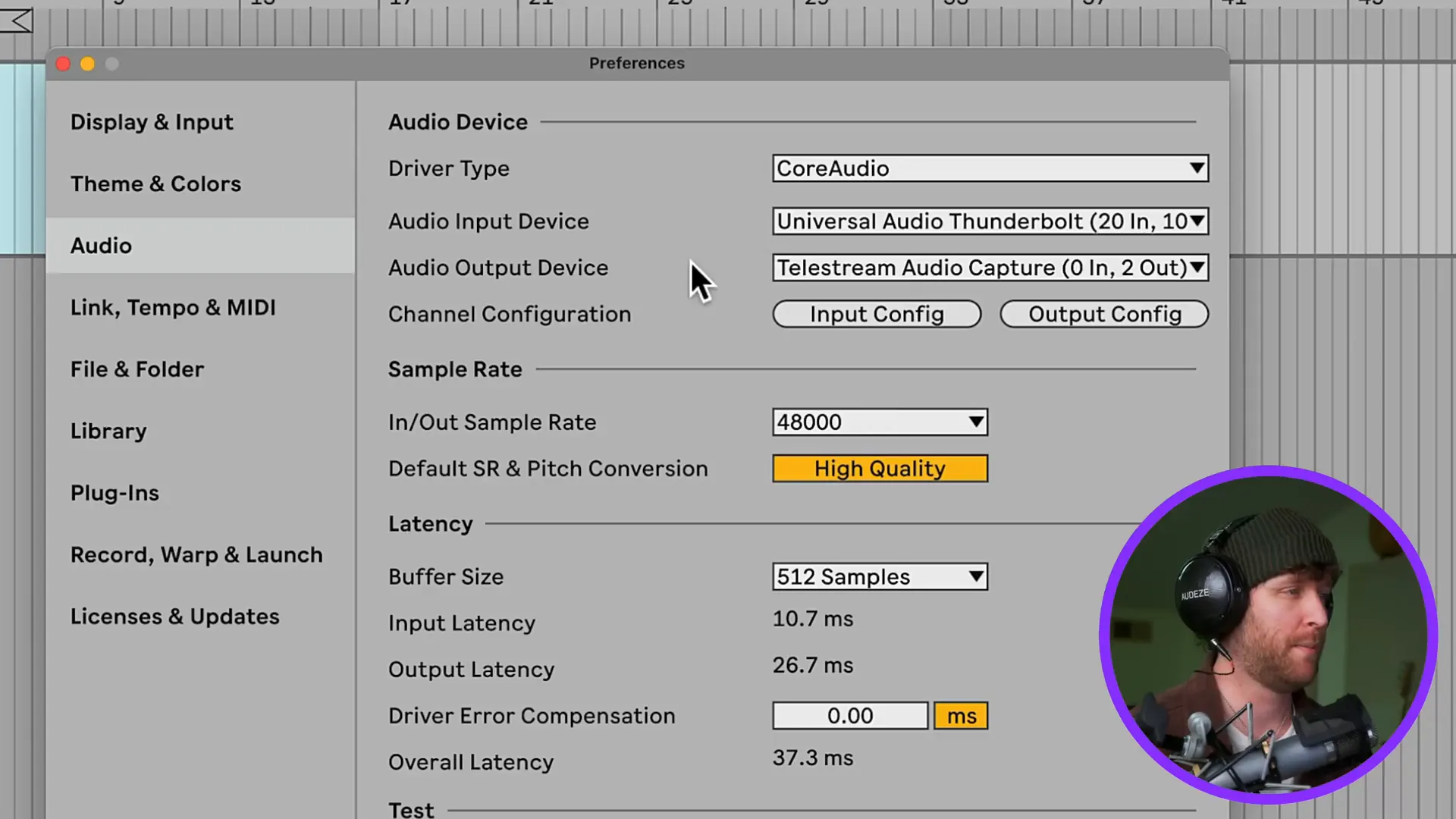
When you create music in Ableton, the experience can be significantly improved by the optimization of your settings. In the Preferences menu, you should start with the Audio tab. Choose your audio interface and set the buffer size. A buffer size of around 256 to 2048 is suggested, which is determined by the performance of your system. When you run into glitches, the solution is to increase the buffer size.
Subsequently, in the File/Folder part, switch off Create Analysis File. Below Record/Warp/Launch, confirm that Auto Warp Long Samples is marked as disabled, unless you want automatic warping.
Understanding the User Interface
The Ableton interface features a very efficient design. The essential segments of the interface are running Music, Session View, Arrangement View, and Browser. The left-sided Browser serves as a navigation to your instruments, samples, and effects. Realizing their mechanics is of significant importance for laying down a good flow.
It is enough to push the Tab key to go back and forward between the views. The Session, on the other hand, permits you to trigger clips and loops, while the Arrangement View brings your song’s linear arrangement. Getting used to the aforementioned views will make it easier to modify your working process.
Exploring Ableton Views: Session and Arrangement
The Session View is specifically designed for improvisation and live performances. You can start the clips in a non-linear way, so it is super suitable for making beats spontaneously. On the other hand, the Arrangement View is where you can put your song in order and make the necessary modifications. Here, you can have your entire set of tracks presented horizontally about the passage of time, which simplifies the tasks of editing and arranging your music.
WEBSITE RESOURCES FOR MUSICIANS
Jumping from one perspective to another will increase one’s creativity. Exploit Session View for exploration and Arrangement View for specifying detailed work. This is the duality embodiment of Ableton that makes it so famous.
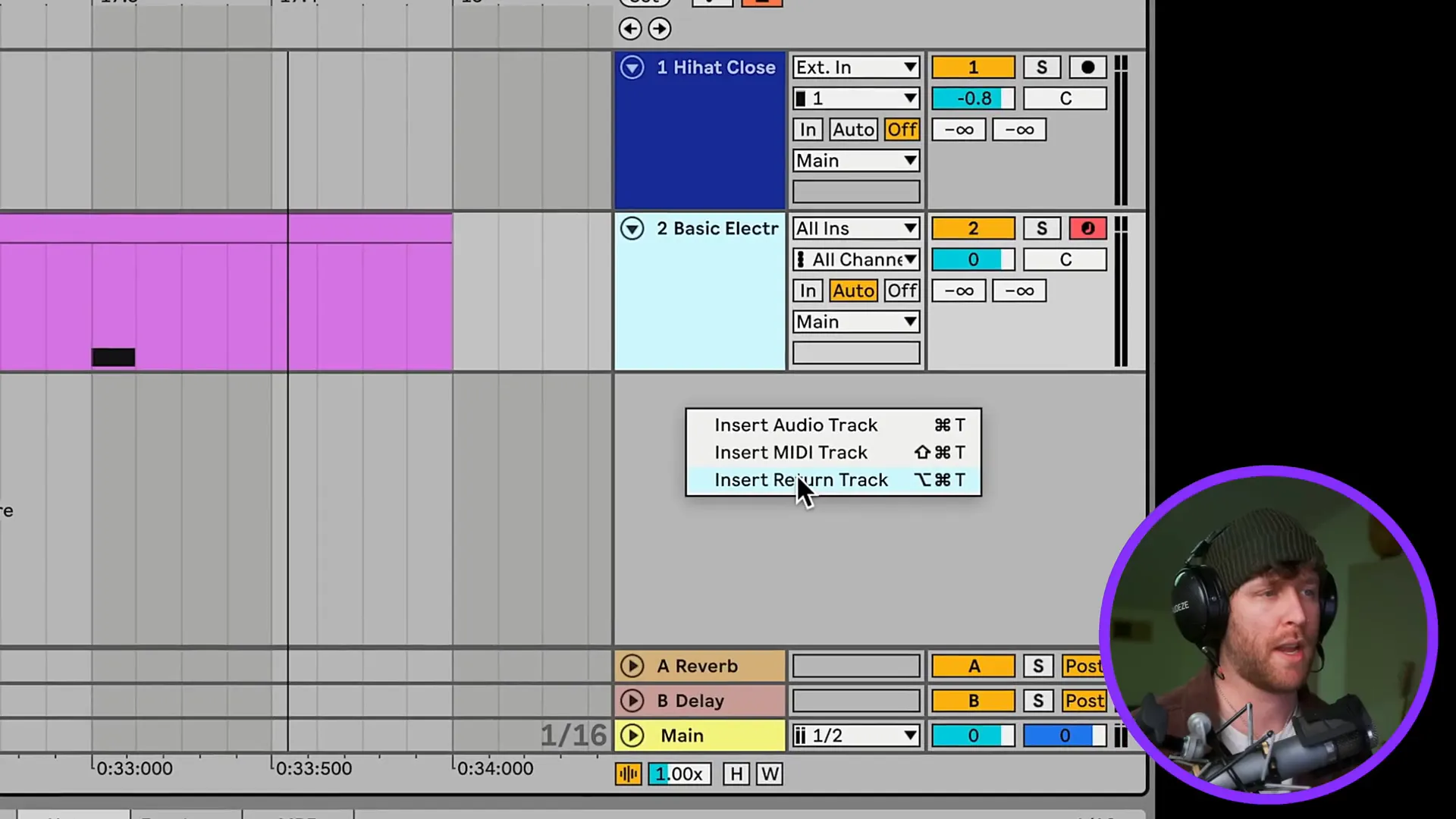
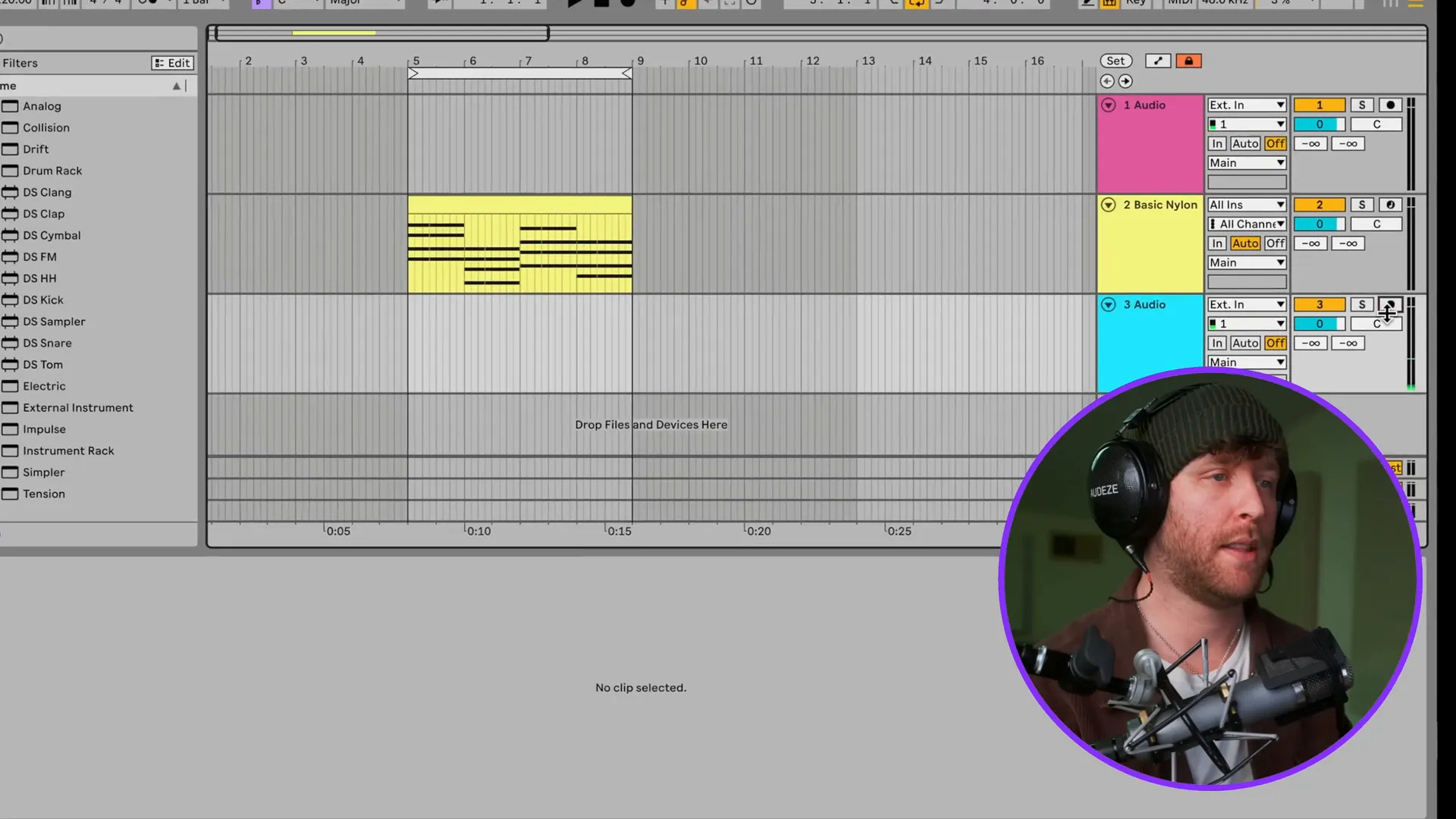
Types of Tracks in Ableton
In Ableton, the three superior track types include audio, MIDI, and return tracks. Audio tracks are for recording and manipulating audio clips, while MIDI tracks are for virtual instruments. Mixing tracks are for controlling the audio routing between different instruments in a project. Learning these tracks well is an essential step in achieving effective music production.
-
- Audio Tracks: Use these for samples and recordings. They’re the backbone of your sound.
-
- MIDI Tracks: These allow you to trigger virtual instruments. You can draw notes in the piano roll to define what your instrument plays.
-
- Return Tracks: These are used for effects. You can send audio signals to these tracks, applying effects like reverb or delay without altering the original sound.
The ability to make elaborate and well-polished tracks will be improved by the effective use of these paths.
Conclusion
We did a lot of things definitely but we must keep in mind that becoming an Ableton master is a journey. By playing with various features and konfigurac you will understand the software much better. As you plung deeper in the art of music making don’t think twice about checking other education platforms and tutorials to add more to your skills and knowledge.
For more insights on music production, check out our other articles, such as Ramzoid 808 Cooker Plugin Review and How Cymatic Made $364,000 Last Month Being Full-Time Producers. These resources can provide valuable tips and techniques as you continue your music-making journey.
Working with Audio and MIDI Tracks
While making beats on Ableton, you need to have knowledge about both audio and MIDI tracks. The tracks are specifically made for different tasks in the music production pipeline.
The audio tracks serve the purpose of recording and manipulating sound clips. You may import samples, recorded instruments, or any audio file. To make an audio track, just click on Command + T.

Unlike audio tracks which record live sounds, MIDI tracks are the ones that are mainly used to trigger virtual instruments. In this way, you can write melodies and harmonies with the help of MIDI data. The MIDI track can be created by pressing the Command + Shift + T keys. After you have created the track, you can add a virtual instrument and input notes with the piano roll.
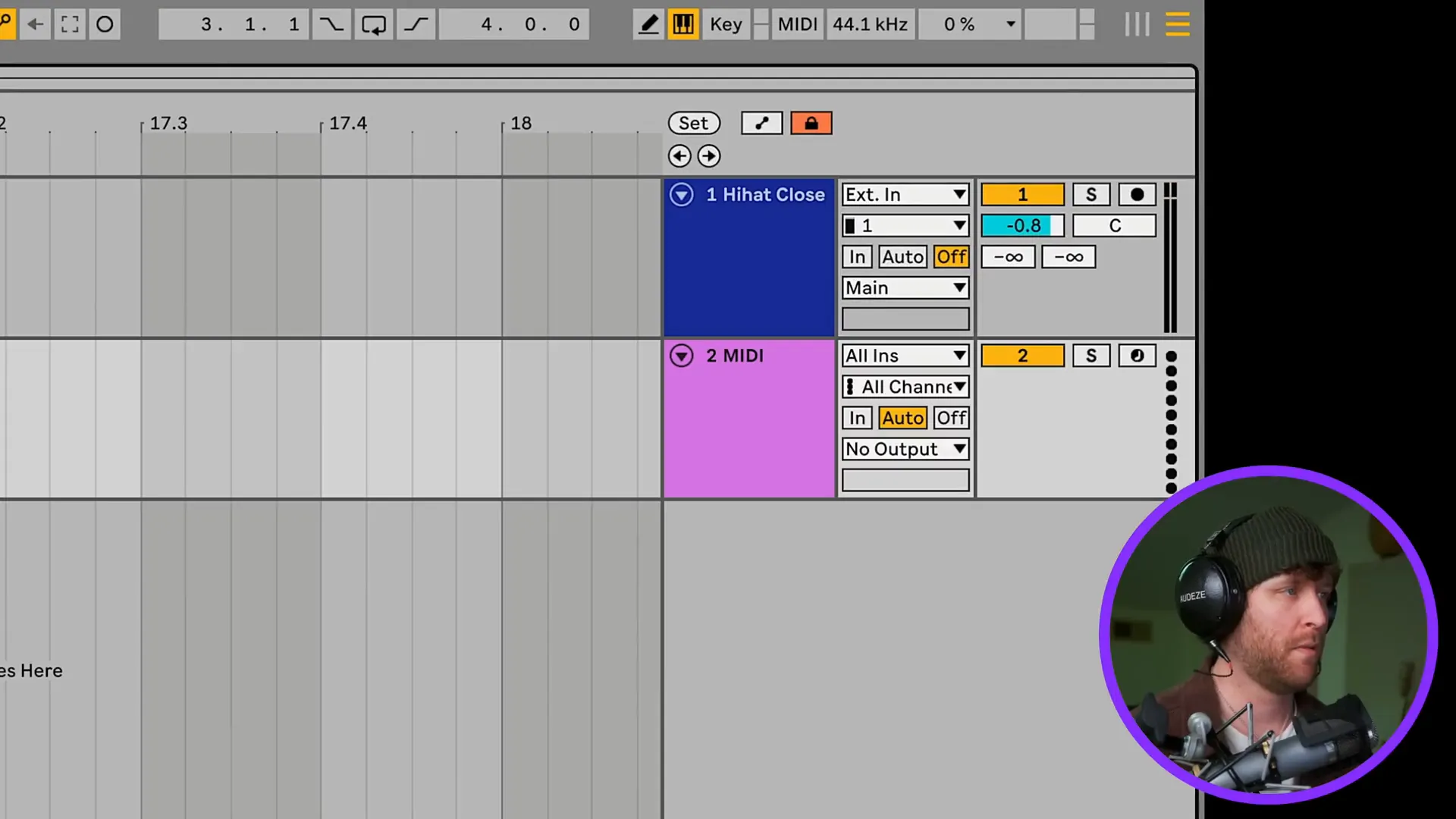
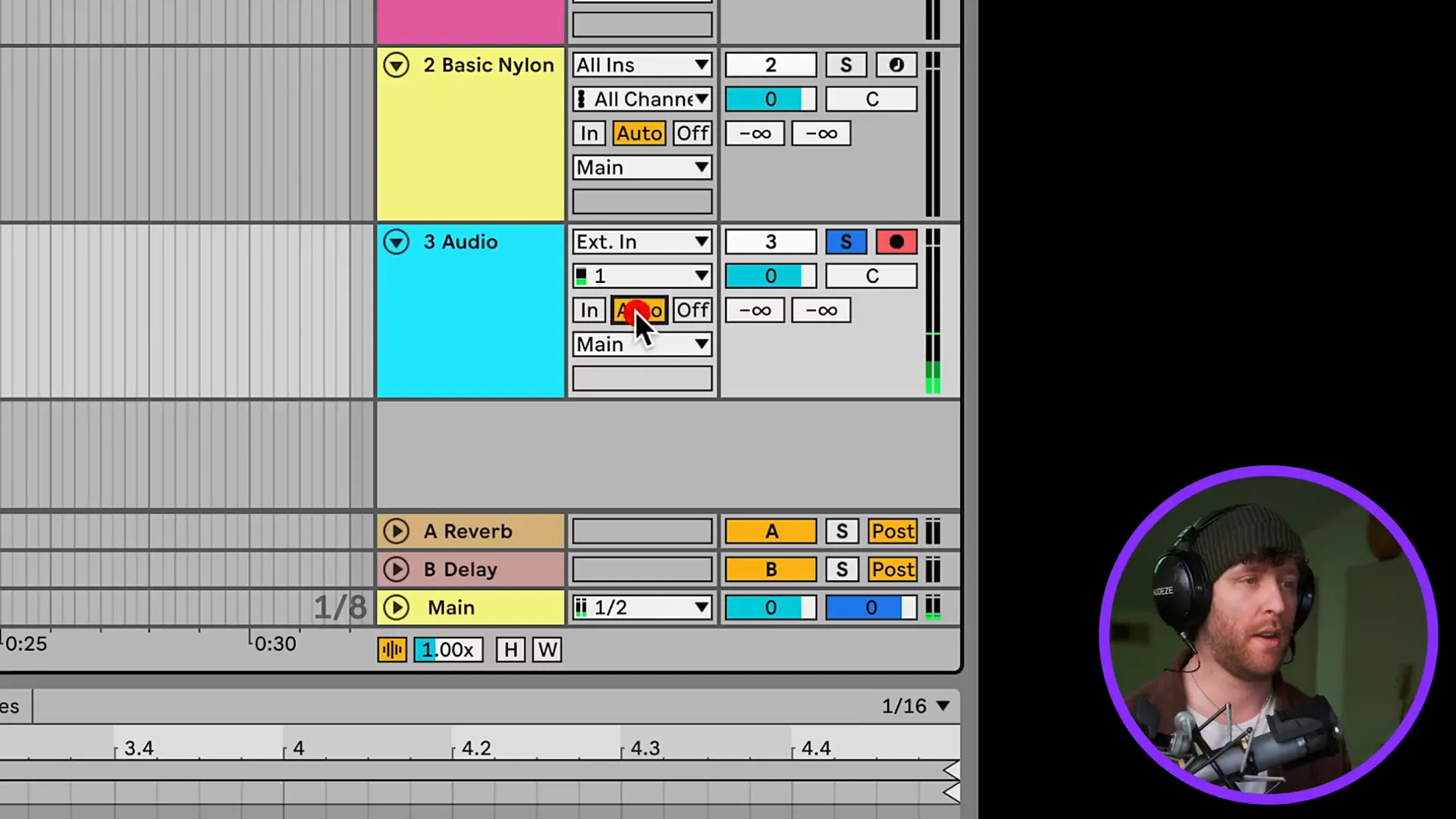
Return tracks, which are also referred to as return channels, are the essential tracks in your workflow which give you the ability to apply effects to many audio tracks without duplicating the effects to each track. Audio signals can also be sent to these return tracks for processing purposes, for instance, for applying reverb or delay to the original audio.
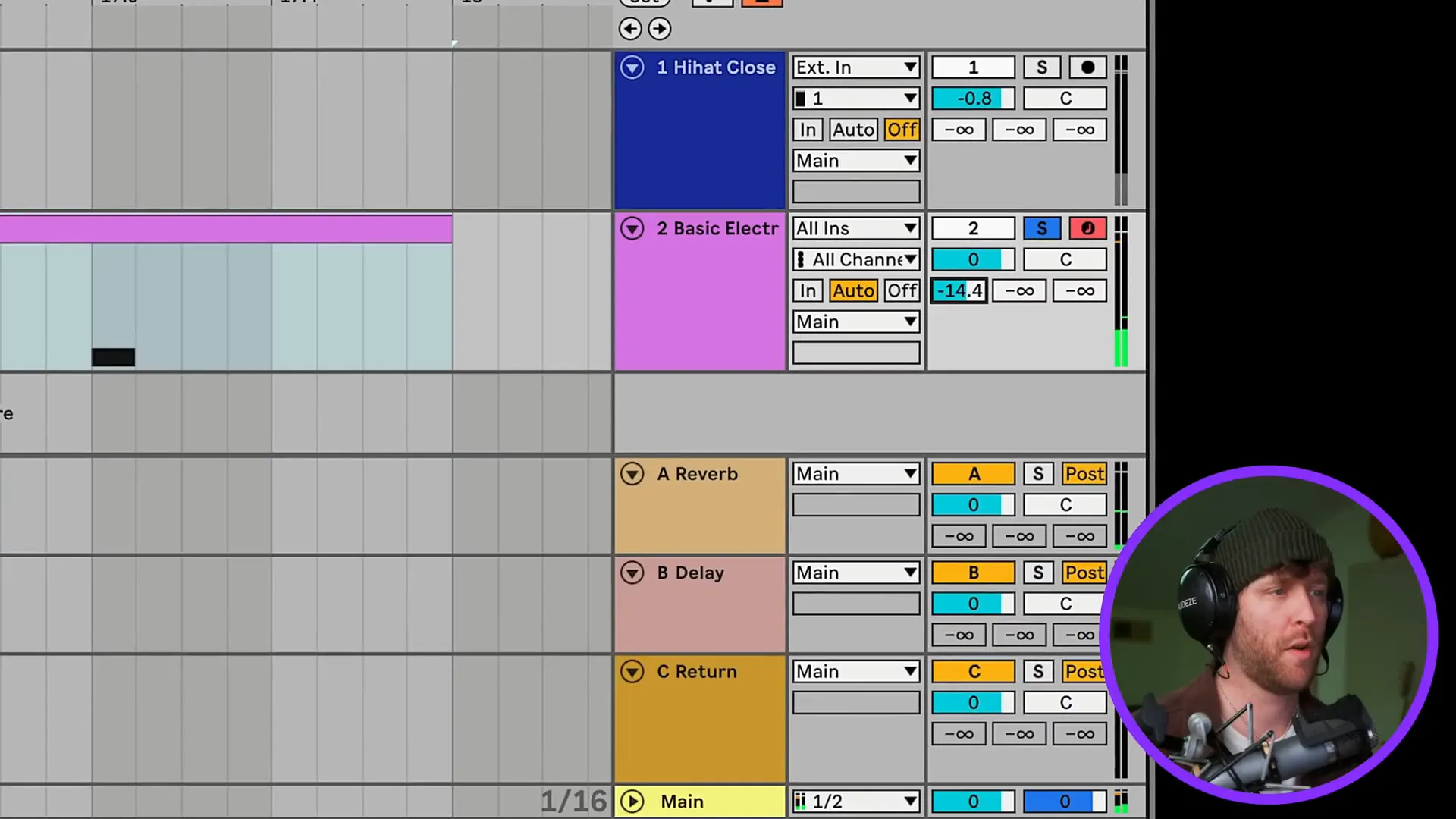
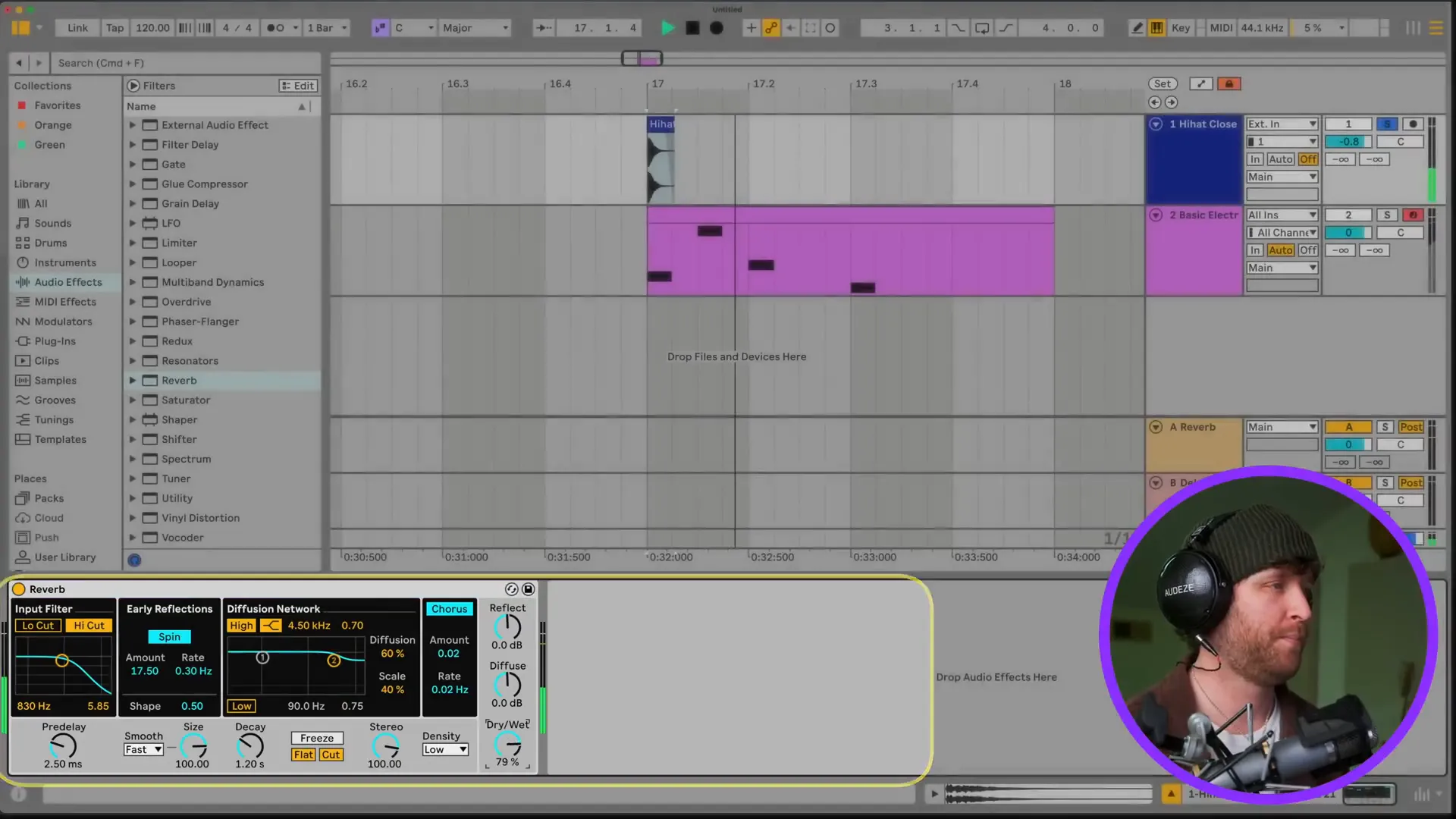
Applying Effects to Your Tracks
Effects significantly contribute to the shaping of your sound. In Ableton, you can either process effects straight to the tracks on their own or route them to the return tracks for a more convoluted processing.
In order to include an effect, just pull it from the Browser and drop it to your audio or MIDI track. For instance, dragging the reverb effect to your vocal track can give you a warm and rich sound that you wanted. And, you can also use return tracks for effects like reverb or delay to keep your original sound intact while improving it.
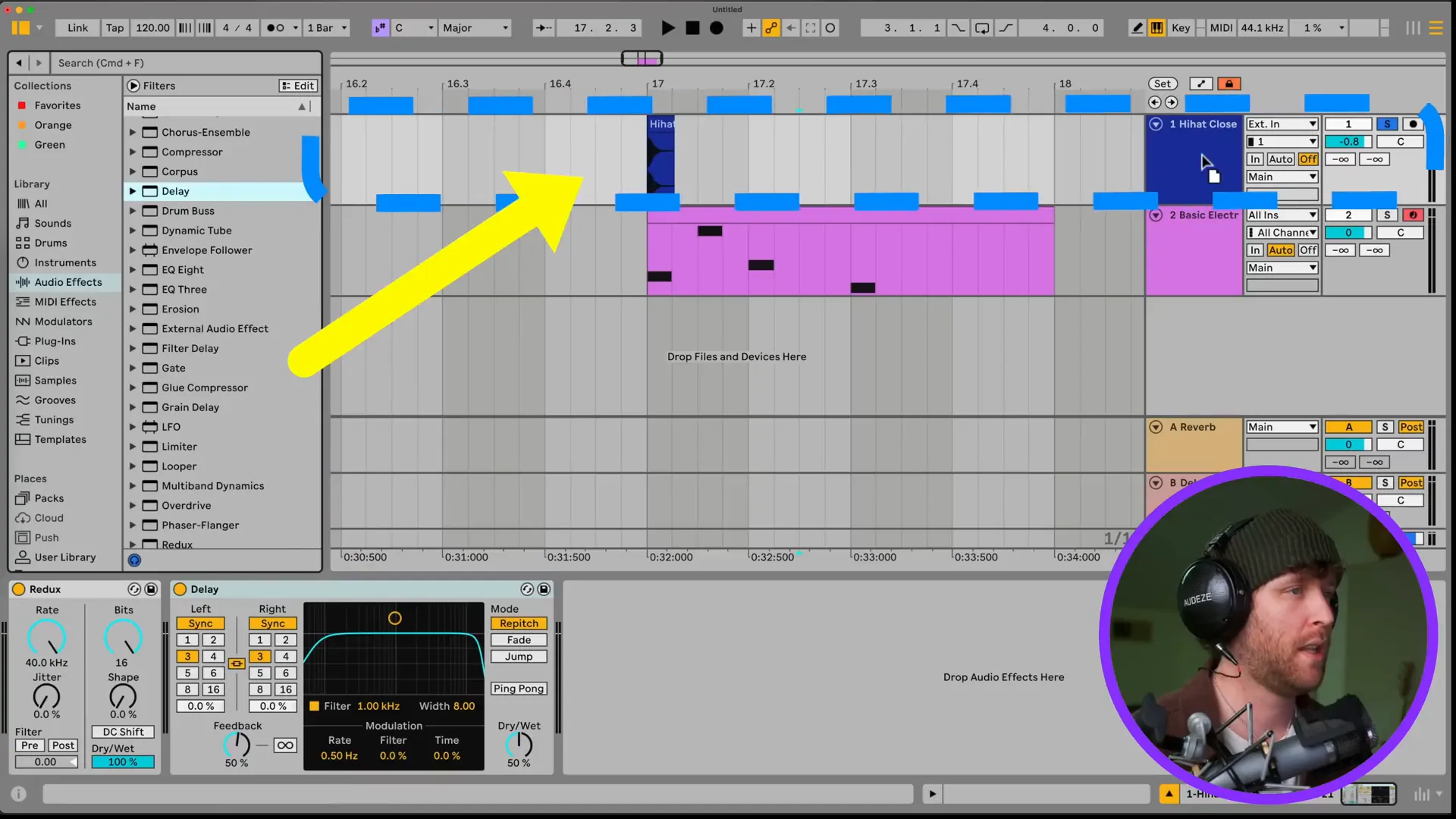
Additionally, you have the option to directly manage the settings of the effects in the view of the track. This level of freedom makes it possible for you to modify the sound and the texture of your music uniquely by trying various tones.
Essential Hotkeys for Efficient Workflow
Streamlining the workflow of your music production is only possible with mastering the hotkeys in Ableton. Below are some essential shortcuts that will cut down the inefficiency of your work:
-
- Command + S: Save your project frequently to avoid losing any progress.
-
- Command + T: Create a new audio track.
-
- Command + Shift + T: Create a new MIDI track.
-
- Command + D: Duplicate selected clips or notes.
-
- Command + J: Consolidate selected clips into one.
-
- Command + E: Slice selected clips at the playhead position.
-
- Command + Z: Undo your last action.
-
- Command + Shift + Z: Redo the last undone action.
By using these shortcut keys, you will be able to work so much faster that you can free your mind from the distraction of looking for the right commands.
Importing Sounds into Ableton
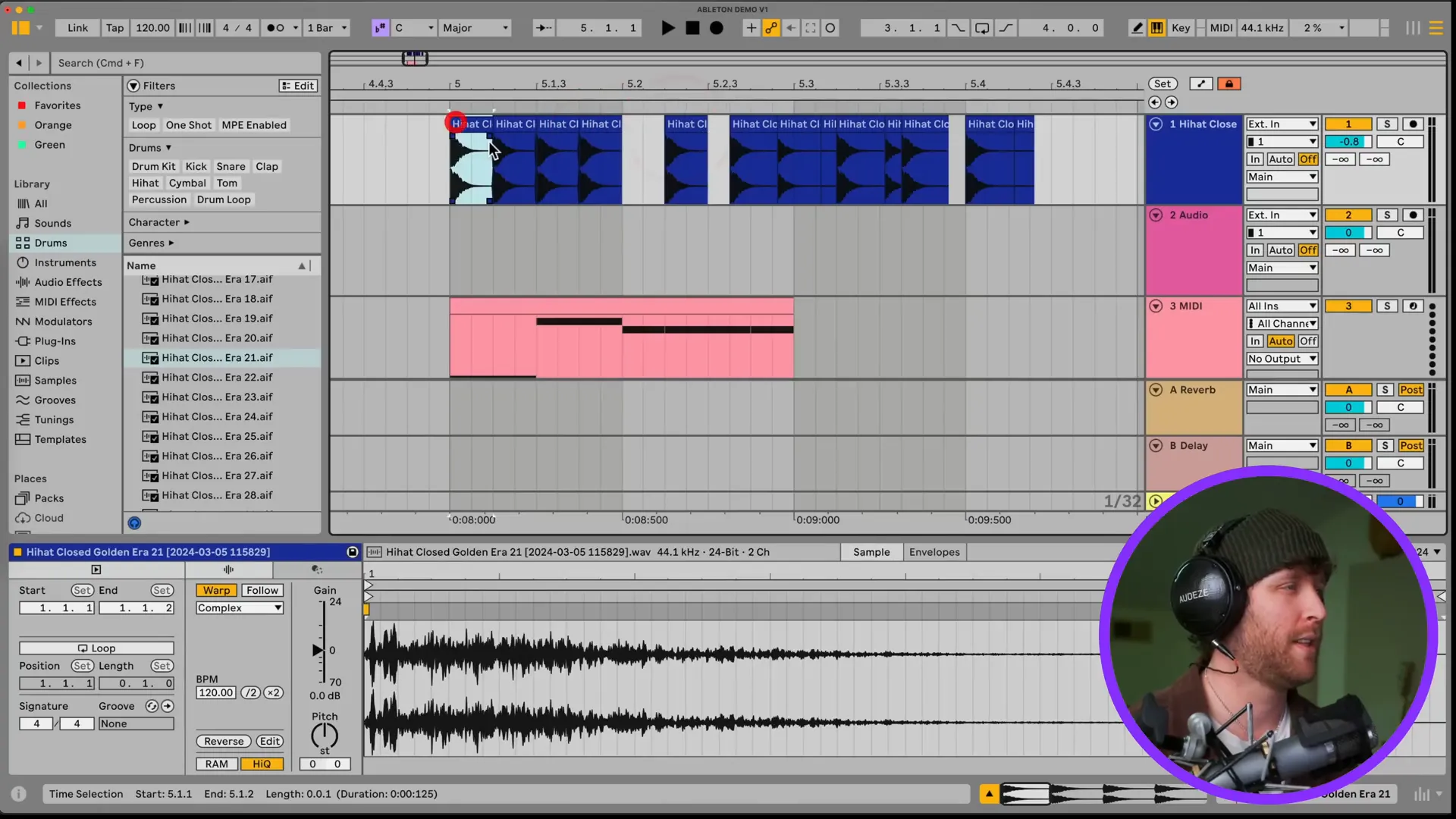
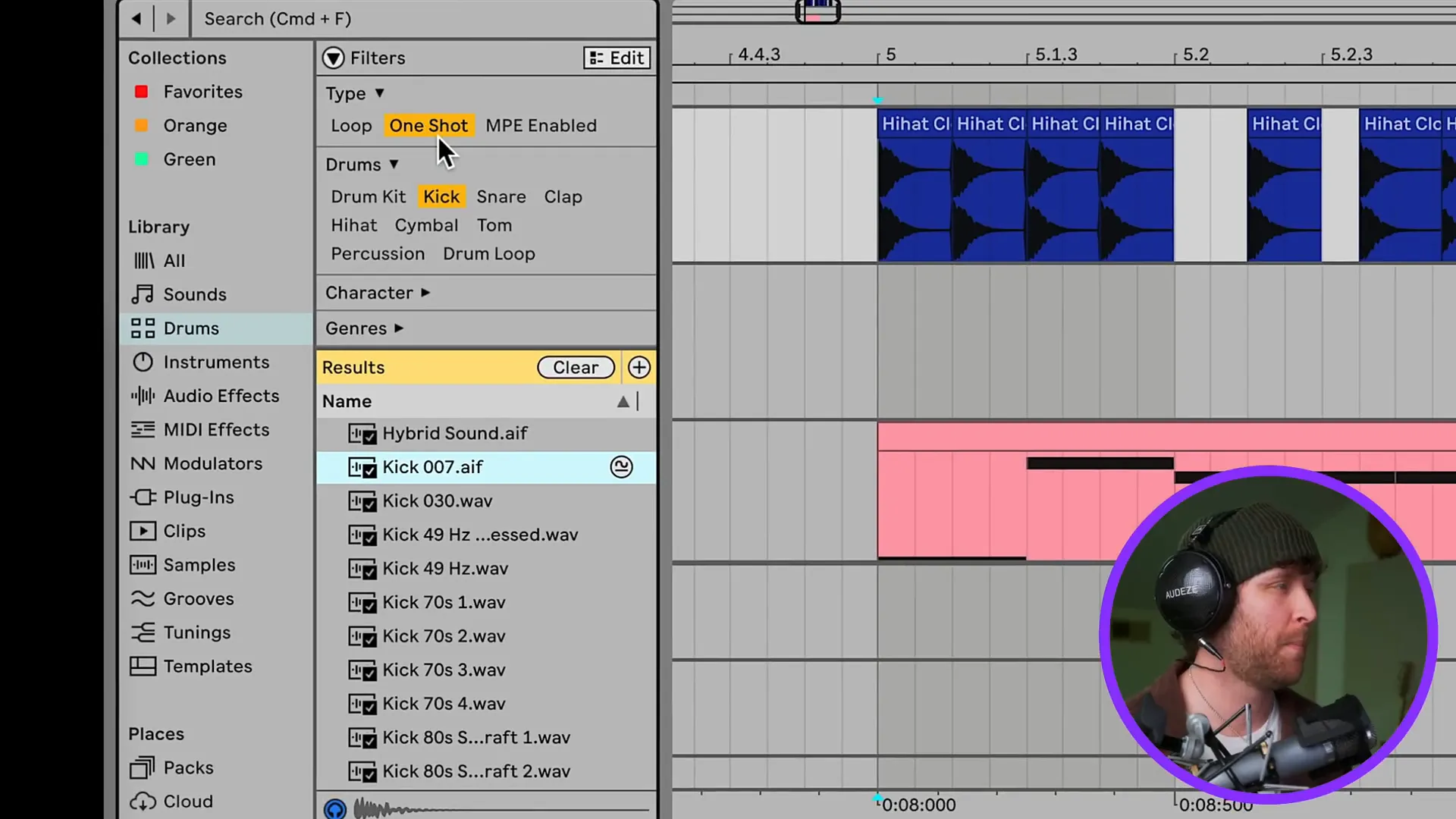
Entering sounds into Ableton is an easy and uncomplicated process. The audio samples can be imported, the sounds can be recorded, or the MIDI can be used to create music.
To bring in audio samples all you need to do is to extract your audio files straight to the session view or arrangement view. In addition, Ableton offers an integrated library of samples that you can scan through.
Recording directly into Ableton is a simple process; just create a new audio track and set it to record. After that, you can press the record button located at the top of the interface to start the recording of your live performance.

When we talk about MIDI, the first thing that comes to mind is the creation of a new MIDI track and the addition of a virtual instrument. After that, you are free to either draw notes in the piano roll view or use your MIDI keyboard to perform them. It is this flexibility that makes it possible for you to compose the most sinuous melodies and complex harmonies with the greatest ease.
Creating Drum Patterns
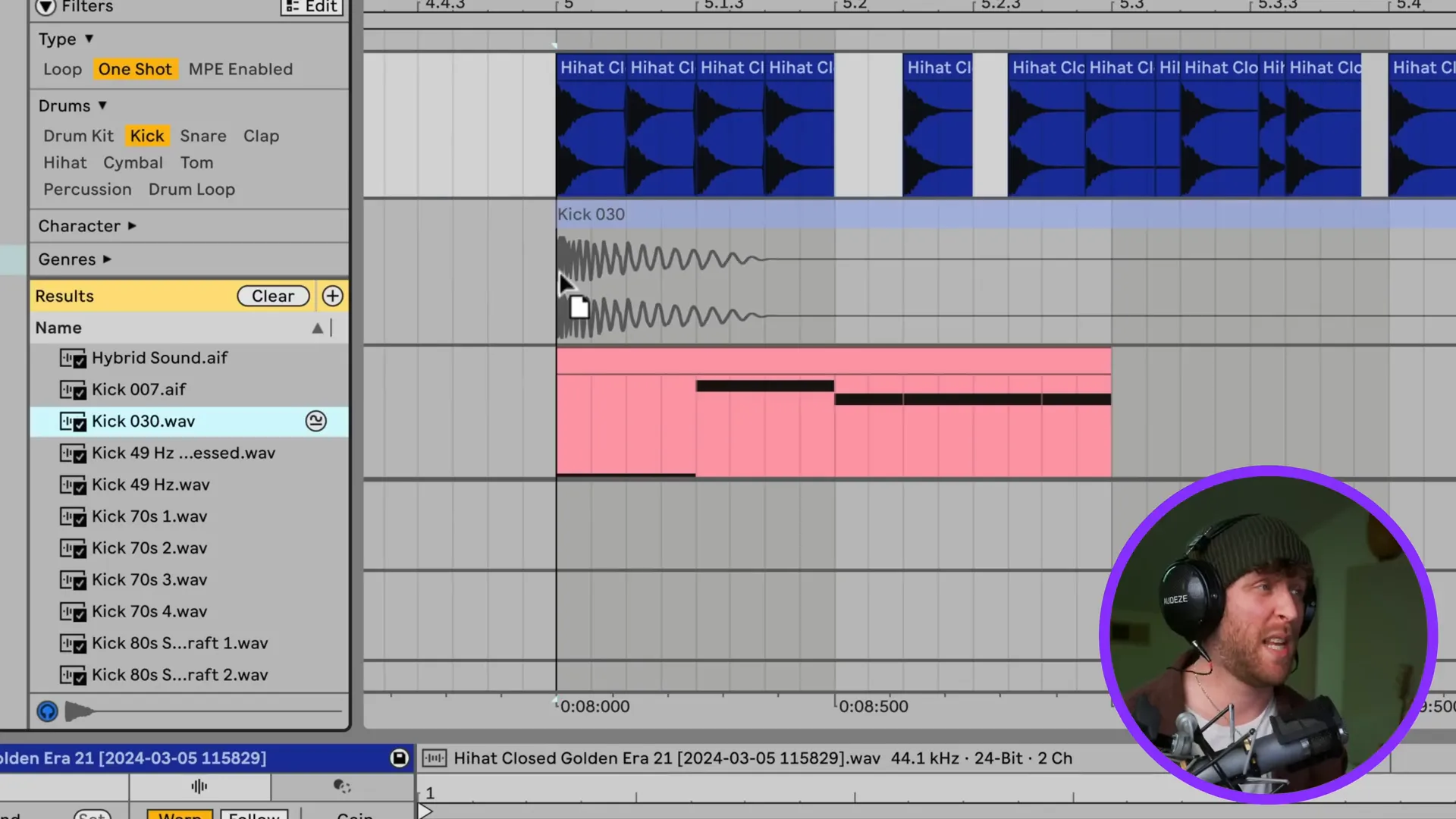
Drum patterns are the foundation for a lot of music types. Ableton can be used to implement an audio sample of complex drum patterns or a MIDI sequence to create them.
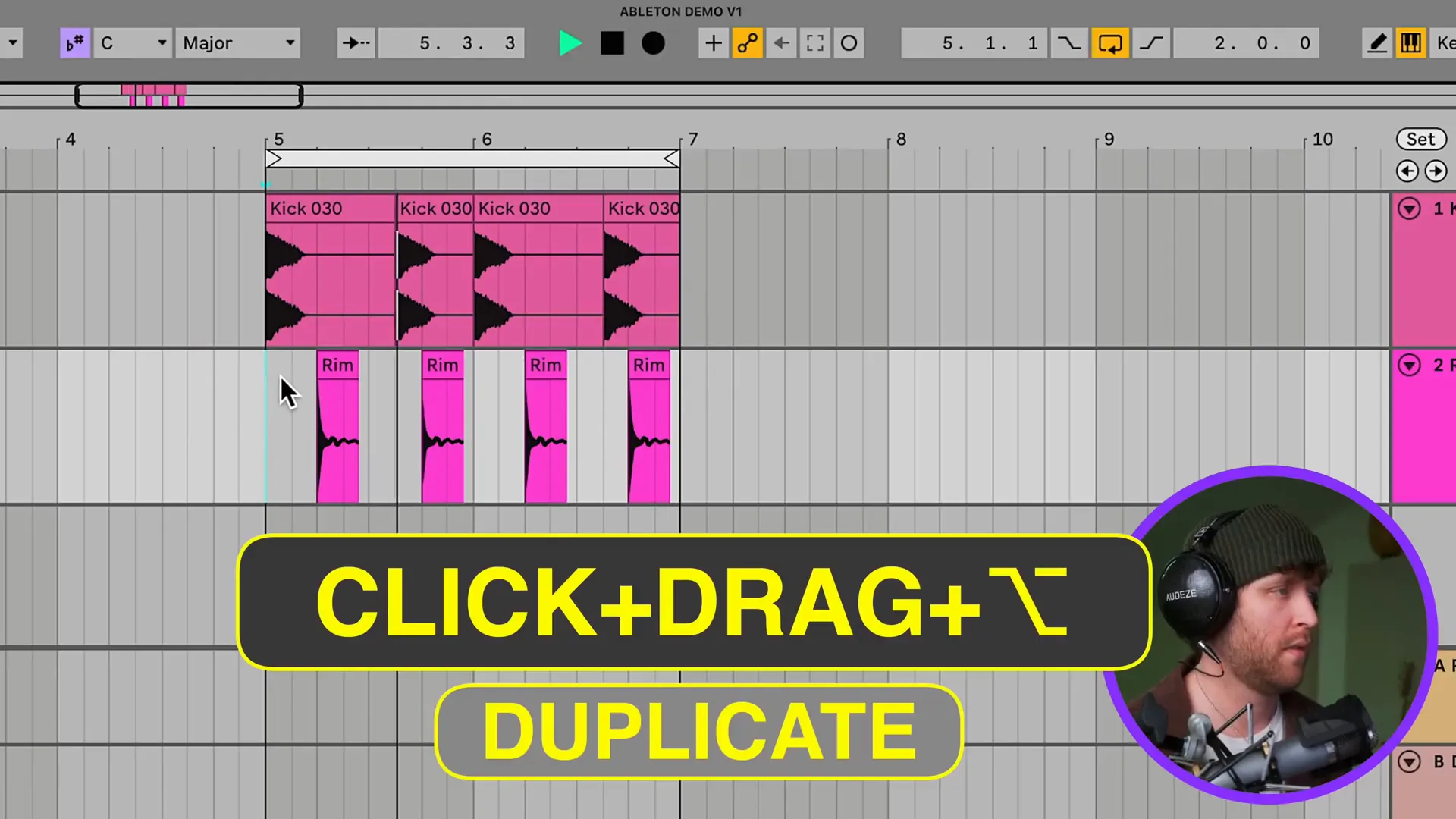
In order to make a drum pattern you have to start by loading your kick, snare, and hi-hat samples into different audio tracks. You can establish a basic rhythm by arranging them in the grid. To create your pattern, you can use Command + D and duplicate the clips.
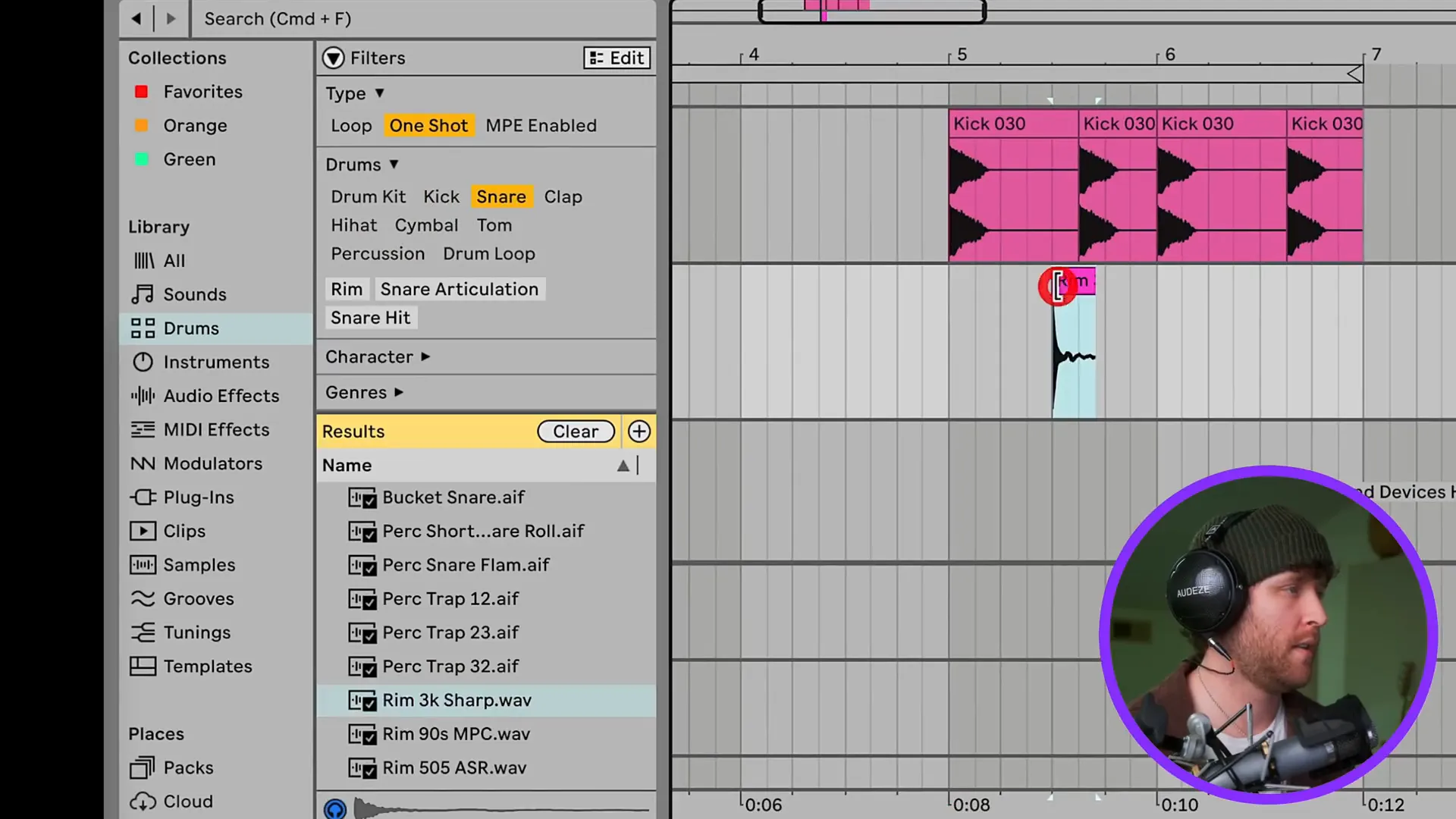
Just click on a MIDI track and add a drum rack if you are using MIDI. Then, you will be able to draw notes into the piano roll to program your beats. This way, you can program the timing and velocity of your drums accurately. As a result, your drums will be properly played.
Utilizing MIDI for Music Composition
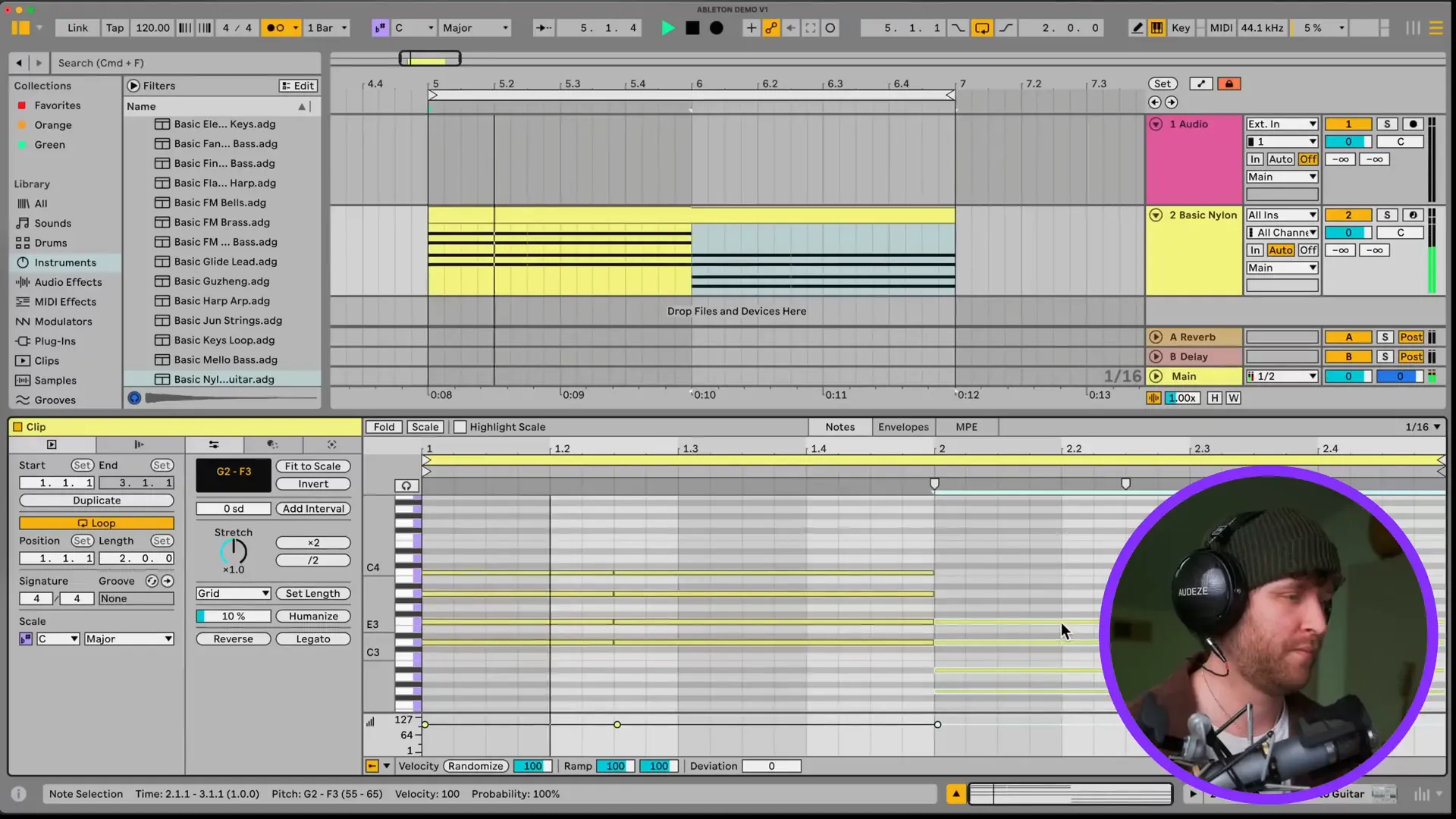
MIDI in Ableton is a strong tool for building and composing music. It enables you to easily create intricate arrangements and control virtual instruments.
To begin the journey into MIDI composing, the first step is to create a MIDI track and then add a virtual instrument. Utilize the piano roll to achieve your goal that is inputting notes; also, it allows you to adjust their length and velocity for dynamic performance. An additional option is to duplicate and paste portions of the original to form variations of your melody.
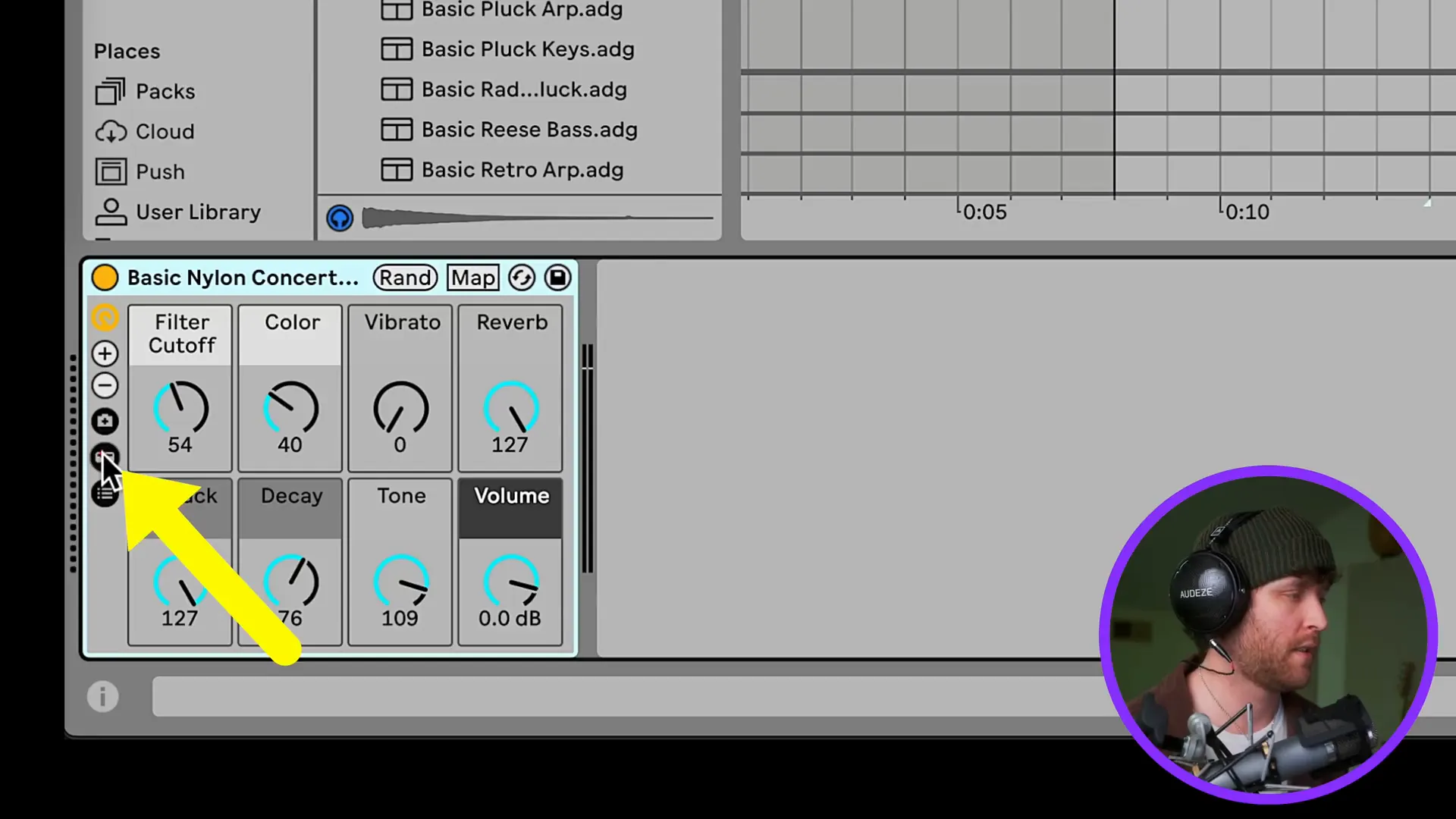
Besides that, the incorporation of MIDI effects in making your compositions more appealing is yet another option. With the help of such effects as arpeggiators or chord generators, your musical ideas can remain rudimentary and interesting. The addition of these items to your equipment could create unanticipated and thrilling outcomes.
Recording Audio in Ableton
Recording audio in Ableton is a simple process that lets you capture your musical ideas in real-time. No matter whether you are recording vocals, instruments, or any sound, the procedures that you have to follow are easy and effective.
Firstly, you need to make a new audio track by pressing Command + T. The track should be armed for recording by hitting the record button on the track. The above mentioned will act as a trigger for Ableton to receive the audio from the microphone or instrument.
After you arm the track, first you need to adjust the signal input levels to clipp out the chances of needing to back off. A good target would be a clear signal that is just above the threshold of the red peak. When the time comes, press the global record button located on the top of the interface and then hit the play button. That will begin the recording for your audio input.

The metronome feature would be a good option to use if you want the recording process to be smooth and effortless for you. Additionally, it is also possible to have a count-in setting to prepare yourself for a brief second before recording. Therefore, you need to first click the metronome icon and then select the count-in option from the drop-down menu to do this.
In the arrangement view, you have the option to make edits to your audio clip directly after recording. For instance, you can cut all the unnecessary parts, apply fades, and change the volume if applicable. You can easily enhance and add the audio tracks to your project with the help of this feature.
Putting It All Together: Creating a Beat
Given the idea that you have already known about the process of audio recording, it’s time to put all of the things you learned together in order to get a complete beat. Beginning with audio samples imported previously drum patterns are formed by simply laying down a drum pattern of your choice. Position the kick, snare, and hi-hat in the grid in order to lay down a good rhythm.
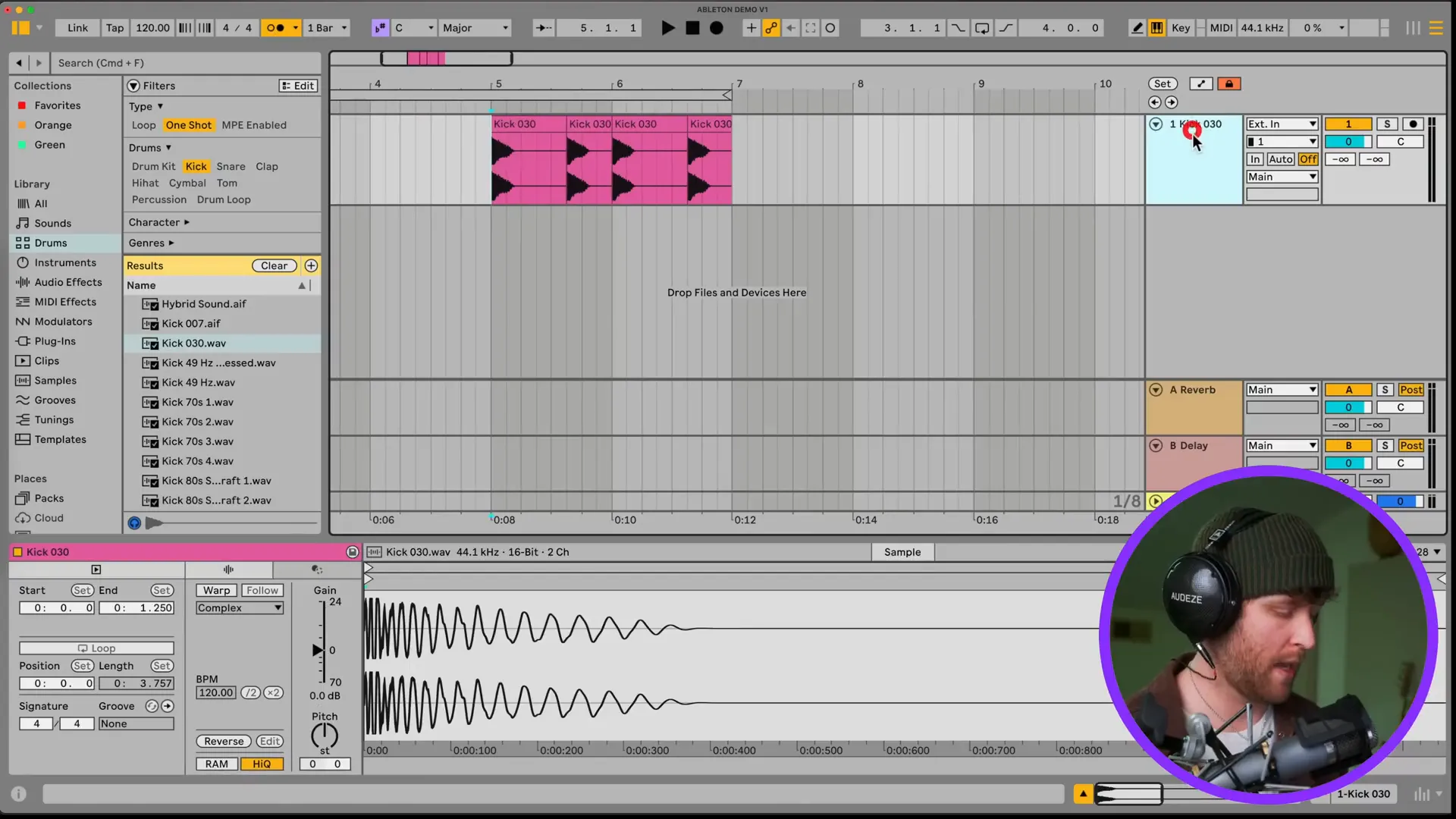
As soon as your drum pattern is set, it’s time to spice it up with melodic elements.Add a MIDI track and select a virtual instrument from the browser. Through the piano roll, you will input notes and you will make a melody that goes well with your drum pattern.
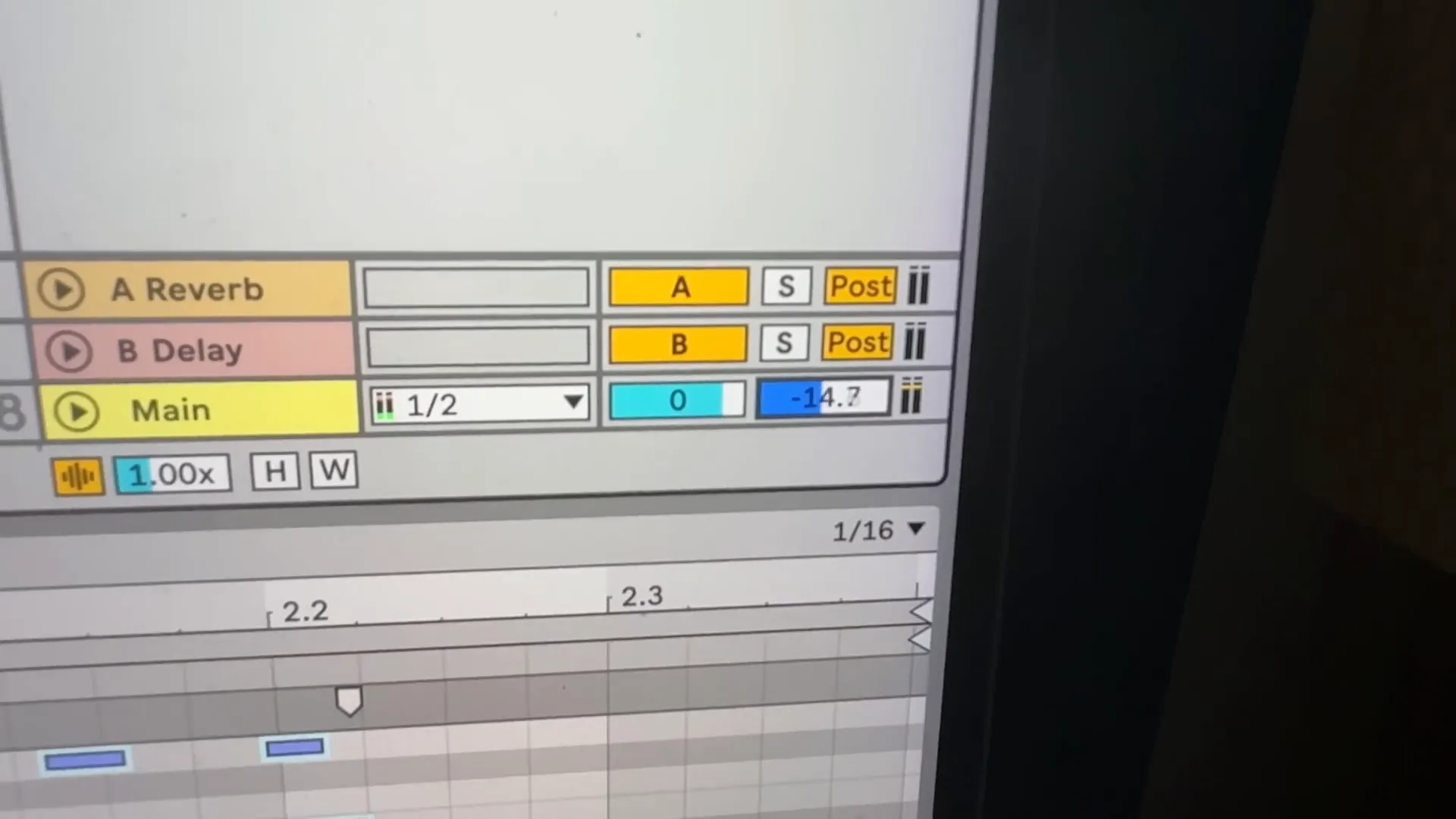
While you are making your beat don, don, don&’t forget to use return tracks for effects. This allows you to use reverb or delay on multiple tracks without changing the original sound. Just send your audio signal to a return track and tweak the effect parameters according to your preference.
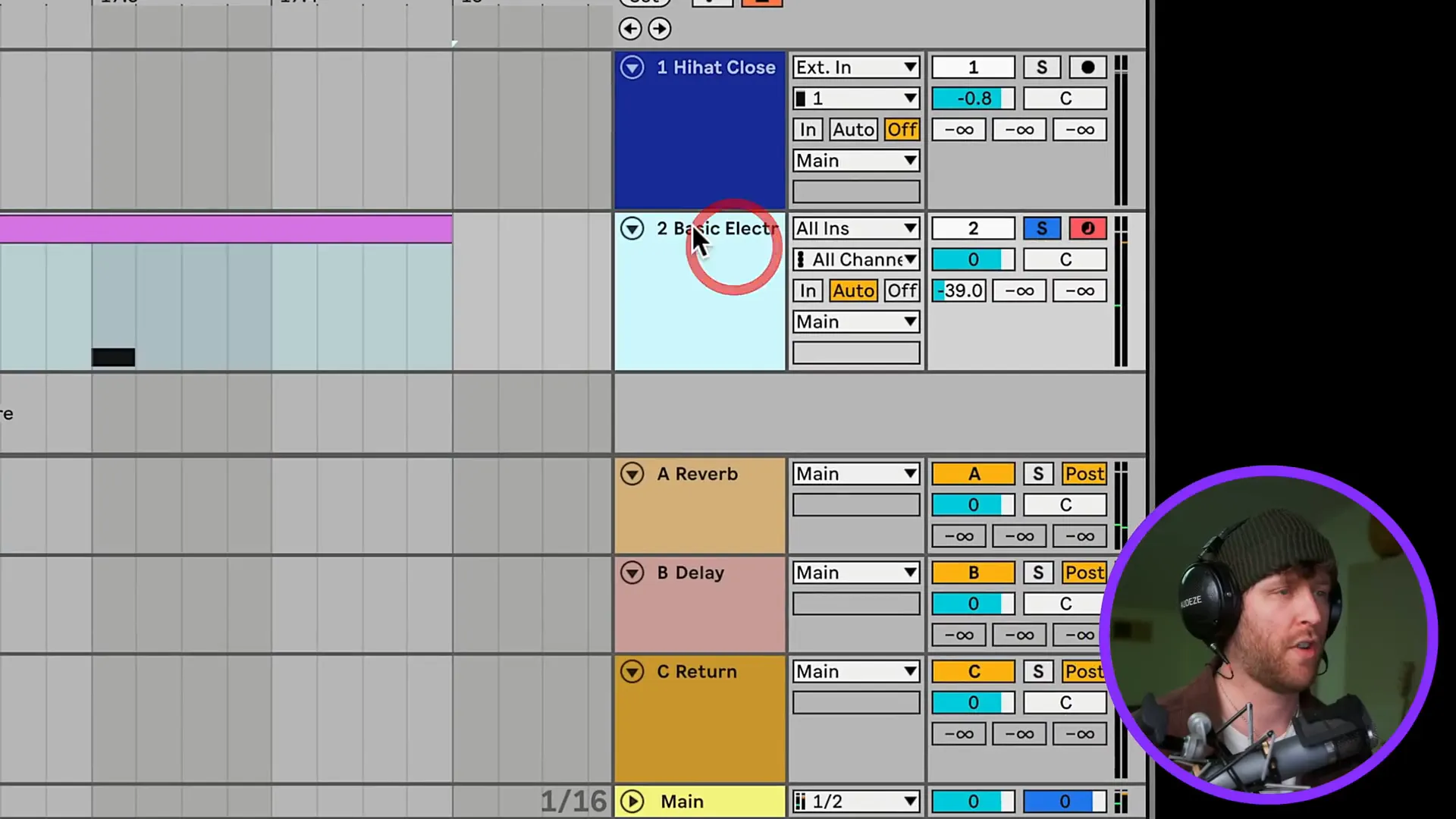
As you develop your composition, dont forget to add the inner instrumentation including bass lines or the synth pads. Try out new and varied samples and MIDI patterns to create a sound that feels truly yours.
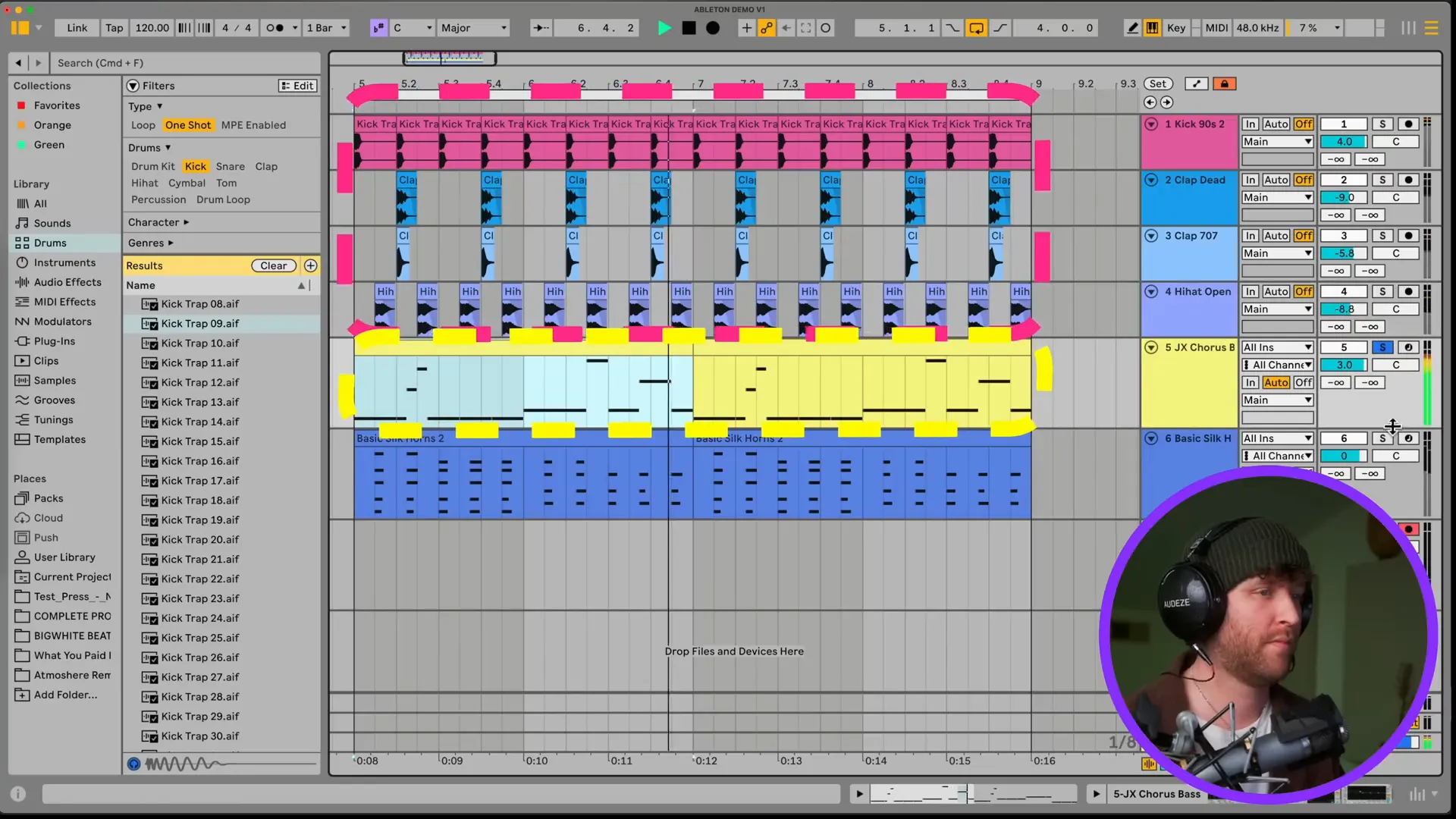
Final Touches: Using Limiters and Saving Templates
Once you finish making your beat, it is very important to put on some final touches to ensure that your beat has a professional sound. A very vital step would be to add a limiter onto your master track. This will help protect your audio from clipping and keep sound quality at its best during playback.
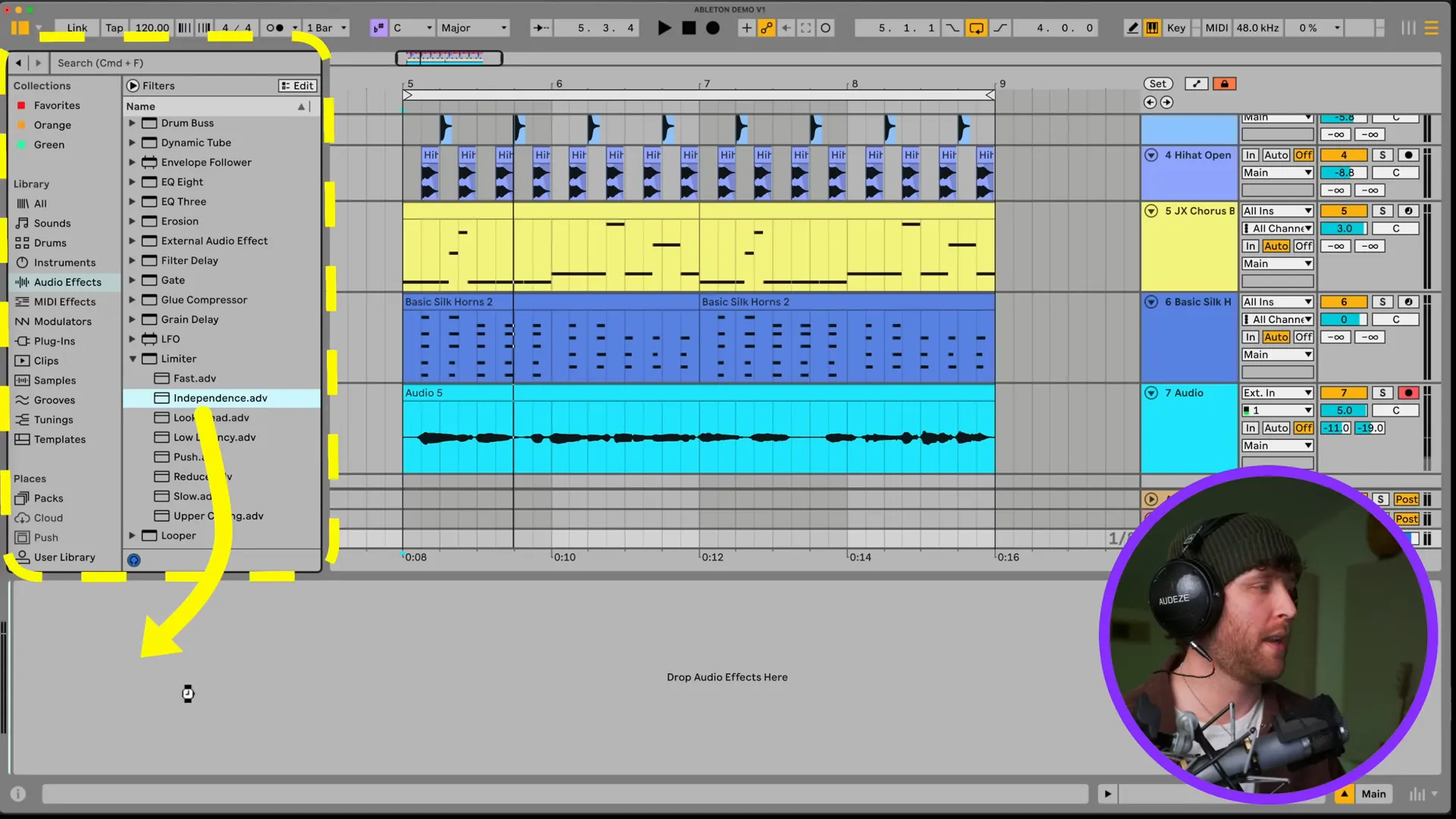
Sure! Here’s your text rephrased: Adding a limiter is as simple as going to Audio Effects and dragging it onto the master track. To prevent distortion, set the gain and ceiling to zero. With this, your track will be able to maintain a constant volume without losing the clarity to a certain degree.
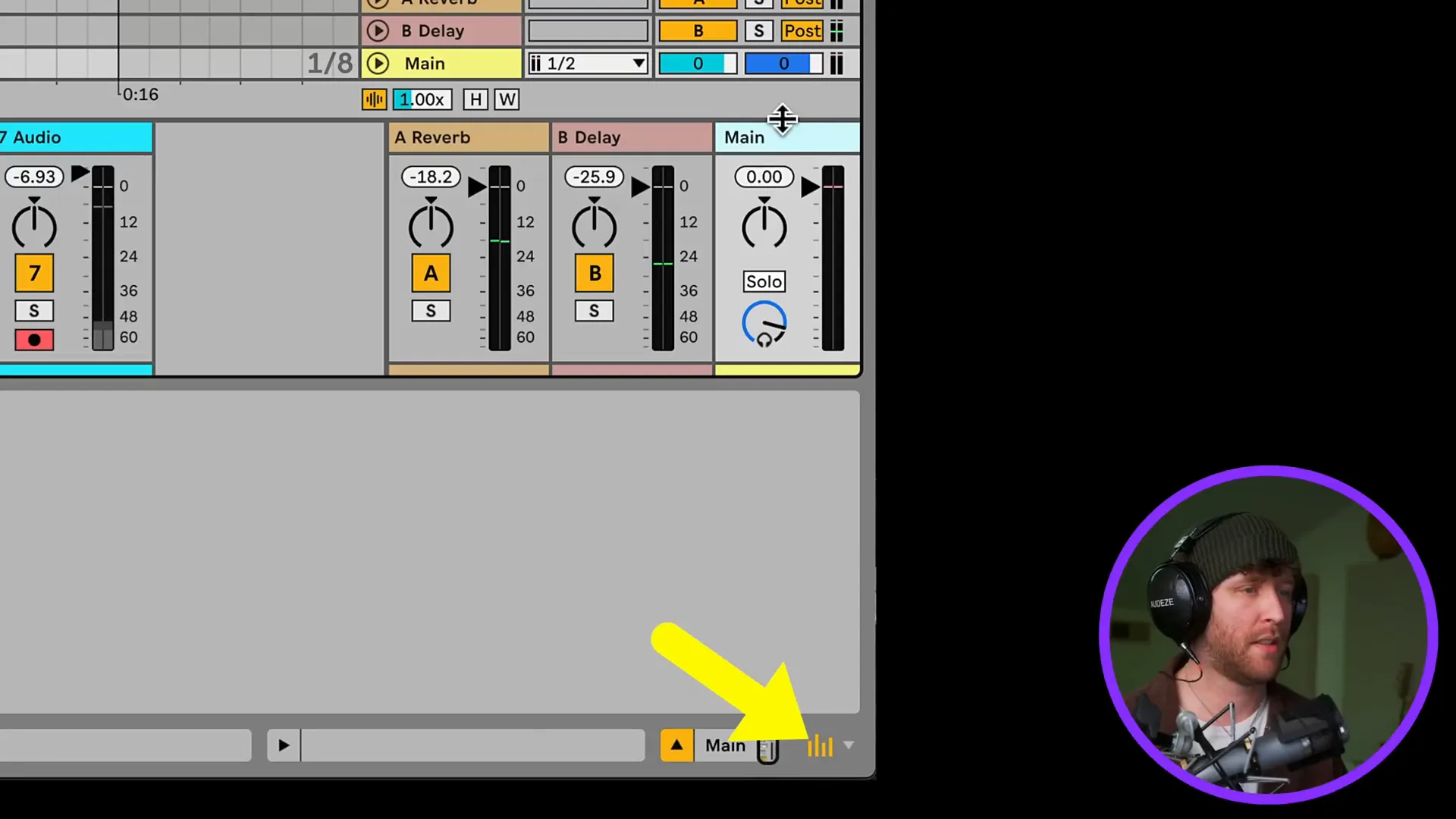
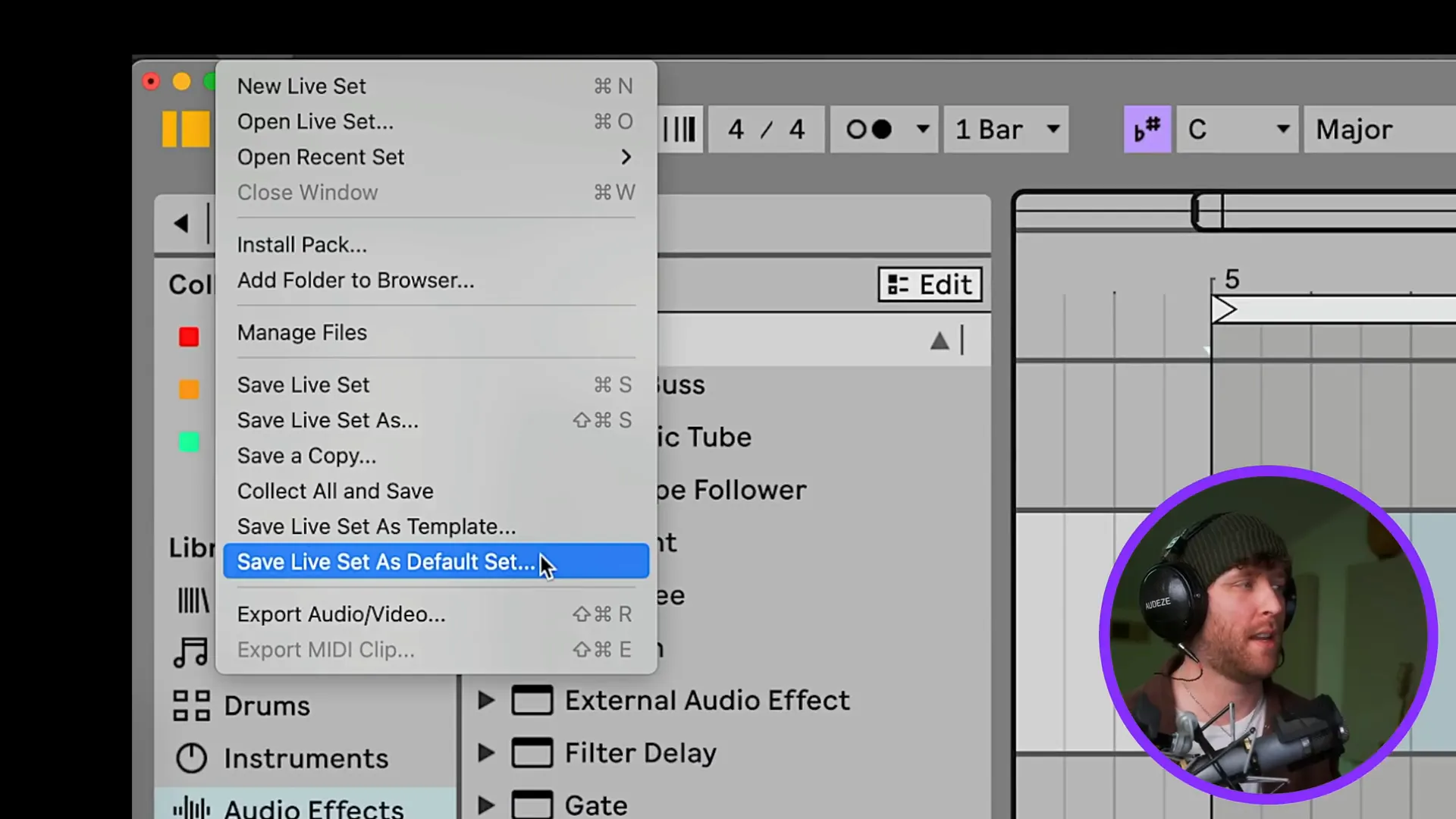
Moreover, you can also save your project as a template closely. This would be quite useful if you have a specific arrangement or effects chain that you use frequently. To do that, you need to click on File > Save Live Set as Default Set. The next time you open a new project, it will automatically load the settings you have chosen.
Conclusion and Next Steps
The fundamental skills needed to create beats in Ableton have been acquired by you. You have already gone beyond the stage of recording audio, layering sounds, and adding effects, and thus, you are well on your way to creating music of professional quality.
As you continue your journey, explore additional resources to enhance your skills. For instance, check out our guide on the Trippie Redd Vocal Effect to learn how to add unique vocal textures to your tracks.
The key to dominions in music production is regular practice, and all sorts of research and experiments. Don’t be shy to go for new techniques and workflows as you perfect your vibe. For any questions or directions needed, reach out or drop a comment below.
Get out there and start creating music! The globe is waiting to listen to your compositions.
